Server Architecture
Biomes server functions are divided across multiple microservices, to be able to scale efficiently according to demand.
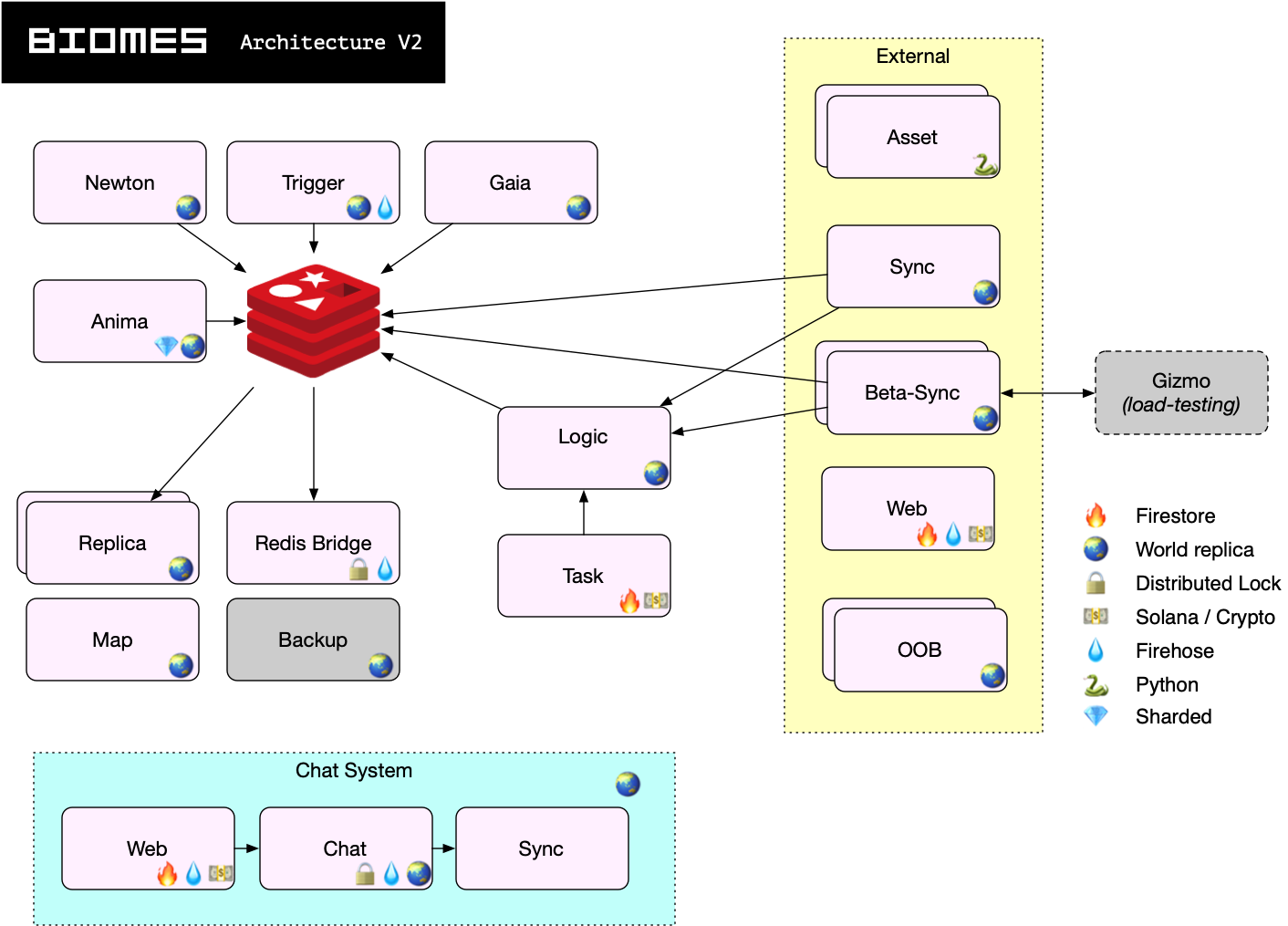
- When a player loads the game, they load a client from the
webserver. - The client then loads assets from the
assetserver, and establishes a connection with thesyncserver to fetch ECS data local to their player's position. - Players' interactions primarily send ECS events to the
logicserver, but can also make calls toweb,chat,oob, andmapdirectly. - Interactions are relayed to players primarily through ECS updates, which are synced to the client with the
syncserver - Other servers are not directly player driven, but changes are made to ECS components that are synced similarly through the
syncserver. An example is thenewtonmoving dropped items independently from any player interactions.trigger,task,newton,anima, andgaiaall fall into the pattern.
When running locally, you can specify a subset of servers that you're interested in running by specifying the server names, i.e. ./b web trigger. Servers will automatically start any servers they depend upon to run correctly.
Servers
Web
- NextJS based Web server
- Serves all API endpoints, the main splash page, and the admin site
- Stateless
Logic
- Runs high-level events for players, typically those that edit terrain
Most player events will create logic server events through ECS.
Logic server events are defined by ECS event handlers in server/logic/events/all.ts
If you are intending to modify or add player-facing game interactions or logic, this is likely the place to start.
Asset
- Is just another copy of the Web server
- Different tier of servers as they have different characteristics due to running Python
- Generates the player mesh
Trigger
- Listens to the Firehose, and has a time-based processor - both are inputs to triggers
- Triggers produce game updates, they:
- Unlock recipes
- Handle quest progression
- Handle expiry / icing / timeouts
Chat
- Uses a distributed lock to maintain a single instance
- Distributes chat messages to sync servers
- Processes a pub-sub feed of chats to guarantee distribution and storage
- Publishes firehose events around DMs
Task
- Processes long-lived asynchronous tasks
- Interacts with Firestore, produces Game events, interacts with crypto
- API is indirect, you schedule tasks by creating them in Firestore
Sync
- WebSocket termination endpoint for clients
- Maintains a copy of the entire world as a replica, serves the relevant parts of this to clients connected to it
- Publishes, on behalf of clients, game events
OOB
- Copy of sync server for directly serving individual entities out of band
- Used for loading distant data to clients
Newton
- Handles drops, their physics and when they get picked up
Anima
- Handles the AI for NPCs in the world, is sharded so each server only handles a subset
Map
- Periodically generates the top-down rendering of the world for the map
Replica
- To eliminate the fan-out cost being directly impacting on the game, anyone who needs a copy of the world shall subscribe to a replica tier
- Maintains a copy of the world, subscribes directly to the World
- Supports the subscription part of the current Game API
Gaia
Gaia authoritively controls all "natural" game simulation in game:
- Lighting
- Muck Creep
- Plant growth and regrowth
- Farming
Redis / Redis Bridge
- Main storage for the world data, and an ability to provide transactions ontop of it.
- Bridge component maps updates that occur in Redis to the Firehose, only one bridge is running at a time.
ETCD
- Distributed locks are maintained using a running etcd server